Summary
Service statuses are used to setup the service states you require, for instance 'Pre-Active', 'Active', 'Suspended' and so on.
In this example we will create a service status type called “Suspended” configured as a “Non-Billable” status so that recurring service charges will not apply while the service is in a suspended state.
For additional details on the fields and options presented on the service status see the Service Status screen help article.
Prerequisites
Service statuses can be setup as needed, there are no prerequisite configuration steps
Sample Configuration
Log into the LogiSense Billing application
Click on the Setup menu, Product Catalog and then Service
Next click on the Service Status tab in the upper right
Click the
 button to add a new service status type
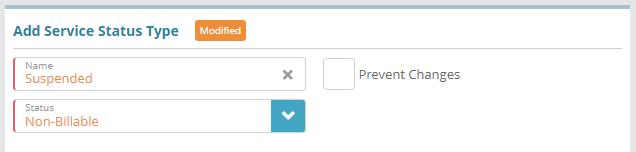
button to add a new service status typeFor the service status type Name enter ‘Suspended’, and in the Status field select ‘Non-Billable’
Click Save to create the service status type
Result
The Suspended service status will now be configurable when configuring services.
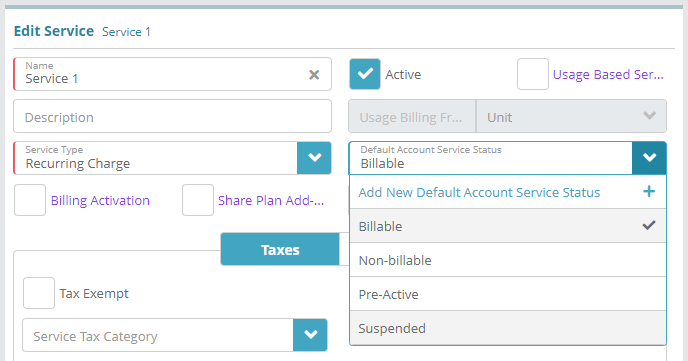
Setup / Product Catalog / Service / Services
The initial or ‘Default’ status that service is set to when it is added to an account can be defined when configuring Services. As shown in the image below, ‘Suspended’ is now in the list of available default service statuses.
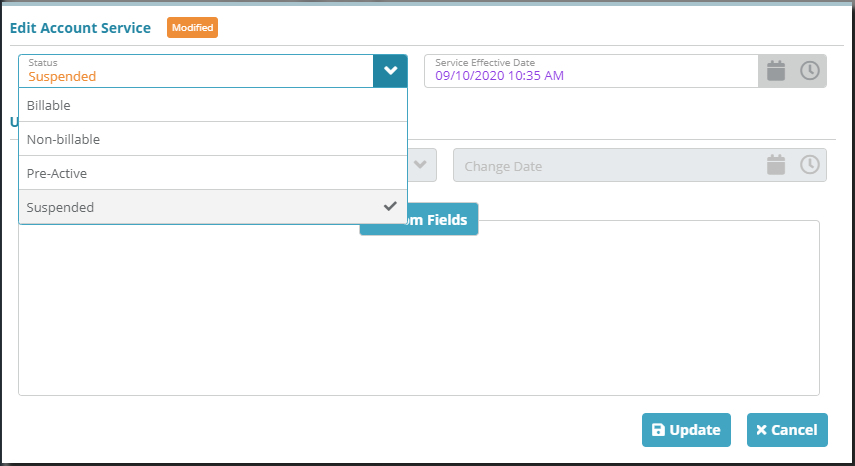
Account / Profile / Packages
The status of the service within an account-package can also be changed. As shown in the image below, ‘Suspended’ is now a status an account-service can be set to.
Next Steps
Optional: Service transitions can be defined if desired so that service transitions charges can be configured on packages (e.g. setup a service transition which allows ‘pre-active’ status services to progress to ‘active’ status services. Once this transition exists it will then be possible to configure an ‘activation’ transition charge on packages). See the Service Transitions Configuration Example article for an example of how to setup service transitions
After service types and statuses have been defined you can proceed to configure services. For an example configuration see the Service Configuration Example article